New computational model reveals novel possibilities for Helicobacter pylori treatment
A new computational model developed by researchers at the Center for Modeling Immunity to Enteric Pathogens (MIEP), Virginia Bioinformatics Institute (VBI), offers new ways to study host immune responses to Helicobacter pylori. Using the model, MIEP researchers identified an abnormal immune response linked to development of lesions during H. pylori infection of the stomach. Their findings may help clinicians pinpoint how best to treat such infections.
“This large-scale computational model of host responses to H. pylori infection combines cutting-edge approaches in computational modeling and experimental research to help elucidate immune responses to H. pylori,” said Dr. Raquel Hontecillas, Co-Director of the Nutritional Immunology and Molecular Medicine Laboratory (NIMML) and MIEP. 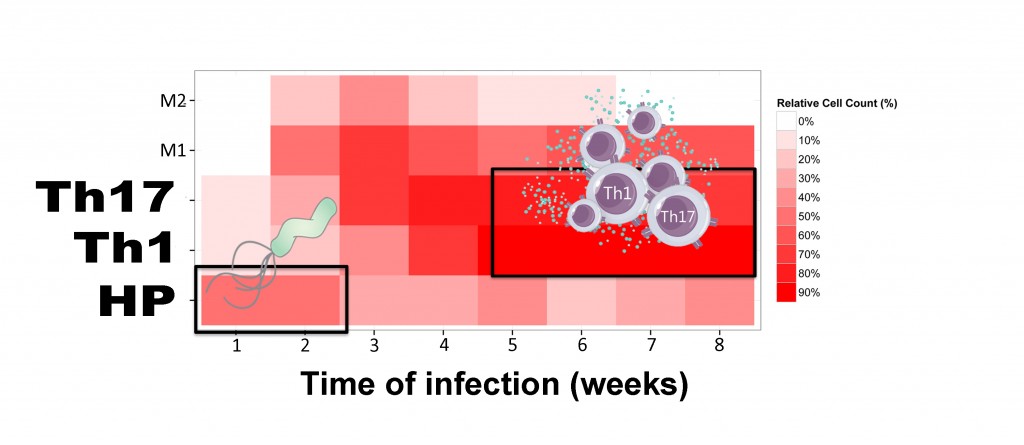 H. pylori is a bacterium that lives in the human gut and sometimes causes ulcers and cancers. Currently, doctors treat H. pylori infections with antibiotics that destroy the bacteria. However, H. pylori also can protect against diseases such as asthma, obesity and diabetes. Understanding how a harmless bacterial population becomes virulent and leads to disease has been difficult, but the computational model developed by MIEP researchers has led to new insights. Based on results from experimental work with mouse models, NIMML researchers built a computational simulation that can predict how and when infection begins and progresses. The model shows the position of cells during infection and accounts for the non-uniformity and randomness of immune responses. Using the computational model, NIMML researchers found that, although H. pylori may be responsible for starting an infection, abnormal immune responses can contribute to chronic ulcers or cancers.
H. pylori is a bacterium that lives in the human gut and sometimes causes ulcers and cancers. Currently, doctors treat H. pylori infections with antibiotics that destroy the bacteria. However, H. pylori also can protect against diseases such as asthma, obesity and diabetes. Understanding how a harmless bacterial population becomes virulent and leads to disease has been difficult, but the computational model developed by MIEP researchers has led to new insights. Based on results from experimental work with mouse models, NIMML researchers built a computational simulation that can predict how and when infection begins and progresses. The model shows the position of cells during infection and accounts for the non-uniformity and randomness of immune responses. Using the computational model, NIMML researchers found that, although H. pylori may be responsible for starting an infection, abnormal immune responses can contribute to chronic ulcers or cancers.
“The knowledge gained from such models will accelerate the development of novel drugs and vaccines for H. pylori-associated diseases,” said Dr. Hontecillas, “The ultimate aim may not be to destroy H. pylori but to learn how to manipulate the interaction of the bacterium and host immune system to produce beneficial effects.”
The paper is available here.
MIEP is funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health, under Contract No. HHSN272201000056C. PI: Josep Bassaganya-Riera.
About NIMML
The NIMML Institute is a 501 (c) (3) non-profit public charity foundation focused on a transdisciplinary, team-science approach to precision medicine at the interface of immunology, inflammation, and metabolism. The NIMML Institute team has led numerous large-scale transdisciplinary projects and is dedicated to solving important societal problems by combining the expertise of immunologists, computational biologists, toxicologists, modelers, translational researchers, and molecular biologists. The Institute is headquartered in Blacksburg, VA. For more information, please visit www.nimml.org or contact pio@nimml.org.
